The Miller Disc counting reticle can be purchased here.
Miller Disc Square Microscope Reticle frequently used to calculate Reticulocytes
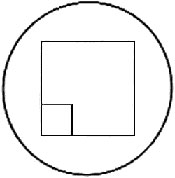 The Miller Disc or Miller Square reticle is used for common counting applications. This reticle enables the operator to determine the number of particles in one of the
The Miller Disc or Miller Square reticle is used for common counting applications. This reticle enables the operator to determine the number of particles in one of the 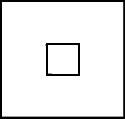 smaller squares on the reticle, then multiply the result to calculate the total number of particles contained within the reticle boundaries. Miller reticles are also useful when comparing the proportion of large to small particles in a specimen.
smaller squares on the reticle, then multiply the result to calculate the total number of particles contained within the reticle boundaries. Miller reticles are also useful when comparing the proportion of large to small particles in a specimen.
The most common use for the Miller Disc reticle is in the reticulocyte count. Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells, typically composing about 1% of the red cells in the human body. Reticulocytes develop and mature in the red bone marrow and then circulate for about one day through the body before developing into mature red blood cells. Reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with specific stains such as new methylene blue.

Reticulocyte
There are multiple methods for performing reticulocyte counts, the most common of which is by using an automated Hematrak device. The National Institute of Health (NIH) performed an analysis of accuracy of reticulocyte counts using various methods such as manual counts with the Miller Disc reticle, ruled reticles, no reticle and compared those results with the automated Hematrack 590 results. Statistical analysis revealed that the Miller Disc reticle method of counting reticulocytes was the most precise and accurate manual method as compared to the Hematrak. By using the Miller Disc reticle imprecision is reduced and the accuracy and precision of manual methods may be increased to that of the automated Hematrak method.
As with any reticle, you will want to calibrate it with a stage micrometer.