Microscopy Polarization Explained
Aug 21st 2018
Polarized Light Microscopy
Polarization contrast is a contrast method to detect birefringence, which is a material characteristic that can be found in minerals, polymers, crystals, pharmaceutical samples, biomedical samples and even botanical samples. Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light.
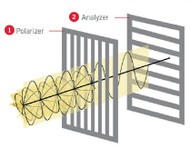
In order to detect birefringence, two polarizing filters are required. The main feature of these filters is that they filter out linear polarized light, which is oscillating in only one direction.
The first filter is called a polarizer (1 in illustration below), and it is placed between the microscope light source and the sample. The other filter is called an analyzer (2 in illustration below) and it is placed between the sample and the microscope eyepieces.
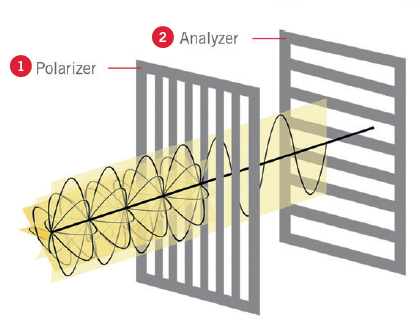
Illustration Courtesy of Motic Microscopes.
When using polarization in microscopy, the analyzer is typically oriented 90º to the polarizer. Once the analyzer and polarizer are aligned perpendicularly a dark background will be produced and any birefringent structure will be displayed as bright or colorful features on this dark background.
In microscopy there are several different types of microscopes that polarization can be used with.
Stereo Microscopes and Polarization:
 Polarization is typically used with a stereo microscope in order to reduce the glare of reflected parts - particularly any metallic parts, circuit boards, or any pieces that are producing a lot of glare. There are two ways to obtain polarization when using a stereo microscope. If the stereo microscope has both reflected and transmitted light, a polarizing set consisting of a polarizer and analyzer can sometimes be added to the microscope. The image above shows a Motic stereo microscope polarizing set where the analyzer shown at left screws onto the body of the stereo microscope, while the polarizer shown at right sits above the light in the stand where the stage plate normally rests. The polarizer can be rotated 360º in order to obtain the desired polarization angle.
Polarization is typically used with a stereo microscope in order to reduce the glare of reflected parts - particularly any metallic parts, circuit boards, or any pieces that are producing a lot of glare. There are two ways to obtain polarization when using a stereo microscope. If the stereo microscope has both reflected and transmitted light, a polarizing set consisting of a polarizer and analyzer can sometimes be added to the microscope. The image above shows a Motic stereo microscope polarizing set where the analyzer shown at left screws onto the body of the stereo microscope, while the polarizer shown at right sits above the light in the stand where the stage plate normally rests. The polarizer can be rotated 360º in order to obtain the desired polarization angle.
 Many stereo microscopes only utilize reflect light (from above the stage). In this case, the alternative way to obtain polarization on a stereo microscope is by using a polarizing LED ring light. A polarizing LED ring light has an analyzer filter that sits inside the ring light and a polarizing filter built into the outside of the LED housing that can be rotated 360º. Again, this allows for obtaining the desired polarization angle to reduce glare.
Many stereo microscopes only utilize reflect light (from above the stage). In this case, the alternative way to obtain polarization on a stereo microscope is by using a polarizing LED ring light. A polarizing LED ring light has an analyzer filter that sits inside the ring light and a polarizing filter built into the outside of the LED housing that can be rotated 360º. Again, this allows for obtaining the desired polarization angle to reduce glare.
Biological Microscopes and Polarization:
When using a biological microscope polariziation is used in biochemistry to detect protein crystals. Researchers will often use polarization when searching for specific types of cells. And botanists sometimes use polarization to view compound structures in plant cells. The medical profession uses polarization to detect gout crystals in urine, however this process not only requires a polarizer and analyzer, but also a first order red wave plate. This kit is explained in a bit more detail below.
 Simple polarization can be added to many compound biological microscopes. Once again, both a polarizer and analzyer are required in order to obtain simple polarization on a biological microscope. In this case, the analzyer is placed inside the head of the microscope (typically between the eyepieces and the objective lenses of the microscope). The polarizer is placed directly over the illumination beneath the stage on the microscope. Shown above is the polarizing kit for the Motic BA210 microscope. It should be noted that on the Motic BA210 microscope, the polarizing set will only work with the halogen version of this microscope, it will not work with the BA210 LED microscope.
Simple polarization can be added to many compound biological microscopes. Once again, both a polarizer and analzyer are required in order to obtain simple polarization on a biological microscope. In this case, the analzyer is placed inside the head of the microscope (typically between the eyepieces and the objective lenses of the microscope). The polarizer is placed directly over the illumination beneath the stage on the microscope. Shown above is the polarizing kit for the Motic BA210 microscope. It should be noted that on the Motic BA210 microscope, the polarizing set will only work with the halogen version of this microscope, it will not work with the BA210 LED microscope.
 Doctors and medical professionals test for gout by using a biological microscope to look for crystals in urine. They perform this gout test by using a compound biological microscope such as the Fein Optic RB40 microscope fitted with a polarizer, analyzer, and first order red (incident wave plate) compensator. Some biological microscopes have a microscope gout kit that is available for use with the microscope such as the Fein Optic RB Gout Kit and the Motic BA410 Gout Kit.
Doctors and medical professionals test for gout by using a biological microscope to look for crystals in urine. They perform this gout test by using a compound biological microscope such as the Fein Optic RB40 microscope fitted with a polarizer, analyzer, and first order red (incident wave plate) compensator. Some biological microscopes have a microscope gout kit that is available for use with the microscope such as the Fein Optic RB Gout Kit and the Motic BA410 Gout Kit.
Polarizing Microscopes and Polarization:
The most common type of microscope that comes to mind when polarization is required is a polarizing microscope. Polarizing microscopes are also known as petrology or geology microscopes. Polarizing microscopes are designed specifically for polarization and are used in fields such as metallurgy, chemistry, geology, petrology, oil exploration, pharmaceutical work and any other field where thin sections of minerals, rocks or birefringent materials must be examined. Polarizing microscopes have a circular rotatable stage, polarizer, analyzer, 1/4 λ plate, sometimes a full λ plate, and a Bertrand lens.
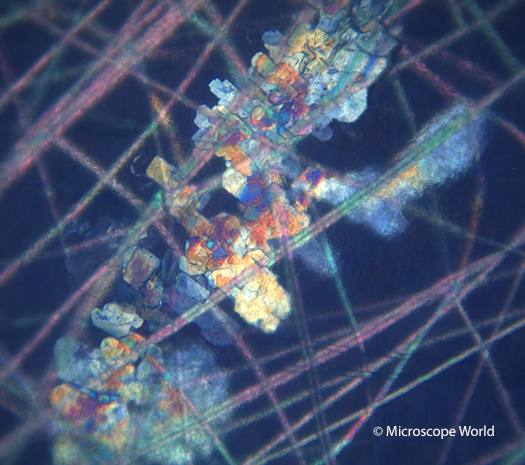
This is an image of polymers captured under a polarizing microscope at 100x magnification.
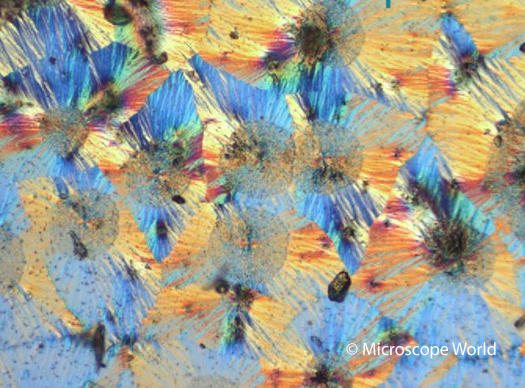
This is an image of Vitamin C captured under a polarizing microscope at 200x magnification.
If you have questions regarding the use of polarization with a microscope contact Microscope World and we will be happy to help.