Below is a list of commonly used stains, often for different types of cells. All those listed can be used on fixed (non-living cells) and any that can be used on living cells are noted at the end of the description with the word "LIVE".
- Bismarck Brown - colors a type of protein called acid mucins yellow. LIVE.
- Carmine - colors animal starch (glycogen), red.
- Coomassie Blue - stains proteins a bright blue, and is often used in gel electrophoresis
- Crystal Violet - stains cell walls purple when combined with mordant. This stain is used in Gram Staining.
- DAPI - a fluorescent nuclear stain that is excited by ultraviolet light, showing blue fluorescence when bound to DNA. LIVE.
- Eosin - a counterstain to haematoxylin, this stain colors red blood cells, cytoplasmic material, cell membranes, and extracellular structures pink or red.
- Ethidium Bromide - this stain colors unhealthy cells in the final stages of apoptosis, or deliberate cell death, fluorescent red-orange.
- Fuchsin - this stain is used to stain collagen, smooth muscle or mitochondria.
- Hematoxylin - a nuclear stain that, with a mordant, stains nuclei blue-violet or brown.
- Hoechst Stains - two types of fluorescent stains, 33258 and 33342 are used to stain DNA in living cells.
- Iodine - used as a starch indicator. When in a solution, starch and iodine turn a dark blue in color.
- Malachite Green - a blue-green counterstain to safranin in Gimenez staining for bacteria. This stain is often used to stain spores.
- Methylene Blue - stains animal cells to make nuclei more visible.
- Neutral/Toluylene Red - stains nuclei red. LIVE.
- Nile Blue - stains nuclei blue. LIVE.
- Nile Red / Nile Blue Oxazone - this stain is made by boiling Nile Blue with Sulfuric Acid, which creates a mix of Nile Red and Nile Blue. The red accumulates in intracellular lipid globules, staining them red. LIVE.
- Osmium Tetroxide - used in optical microscopy to stain lipids black.
- Rhodamine - a protein-specific fluorescent stain used in fluorescence microscopy.
- Safranin - a nuclear stain used as a counterstain or to color collagen yellow.
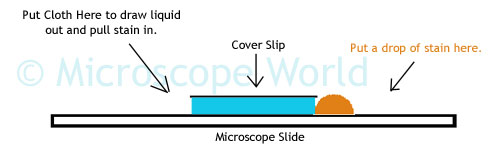
The image above shows how to draw a stain into a prepared slide. With the cover slip in place on top of the specimen, place a drop of stain on the edge of the cover slip. On the opposide side of the cover slip place a paper towel or cloth to draw the liquid out from the cover slip. As the liquid is drawn out, the stain will be pulled in under the cover slip.